When the force f is constant and the angle between the force and the displacement s is θ, then the work done is given by: Energy transferred = work done.
Equation For Work Done By A Force. Keeping in mind that a friction force is a contact force always opposed to a moving force through a surface of contact, i describe here a case i think is rather general. Defined by the following vectors:
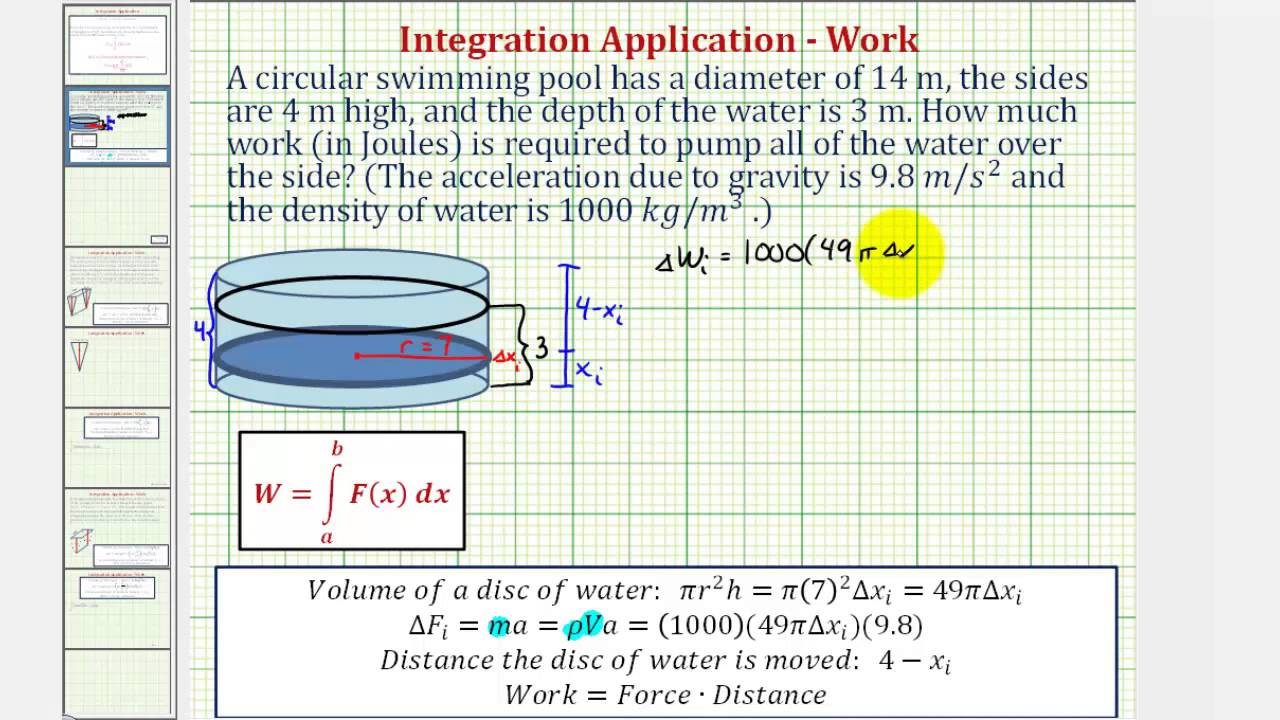
 Ex Determine the Work Required to Pump Water Out of a From youtube.com
Ex Determine the Work Required to Pump Water Out of a From youtube.com
{eq}w=fd {/eq} {eq}w= (2.746\cdot 10^9n) (5.9\cdot 10^ {12}m) {/eq} {eq}w=1.62\cdot 10^ {22}j {/eq} the work done by. Action of this force is to move the body through a distance d in a straight line in the direction of force. W = f ∙ d.
Ex Determine the Work Required to Pump Water Out of a
∫ a b f ( r ( t)) ∙ r ′ ( t) d t. Therefore, w = f x δx. Work is done whenever a force moves something over a distance. It is articulated in nm.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Homework for calc iii includes a problem about computing the work done by a force field (defined by a specific vector equation) on a moving particle. Action of this force is to move the body through a distance d in a straight line in the direction of force. Work is done whenever a force moves something over a distance. F.
 Source: diffen.com
Source: diffen.com
Θ is the angle between force and direction of motion; Defined by the following vectors: If that force is constant then the work done by the force is the dot product of the force with the displacement:. The amount of work a force does is directly proportional to how far that force moves an object. The general formula for work.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
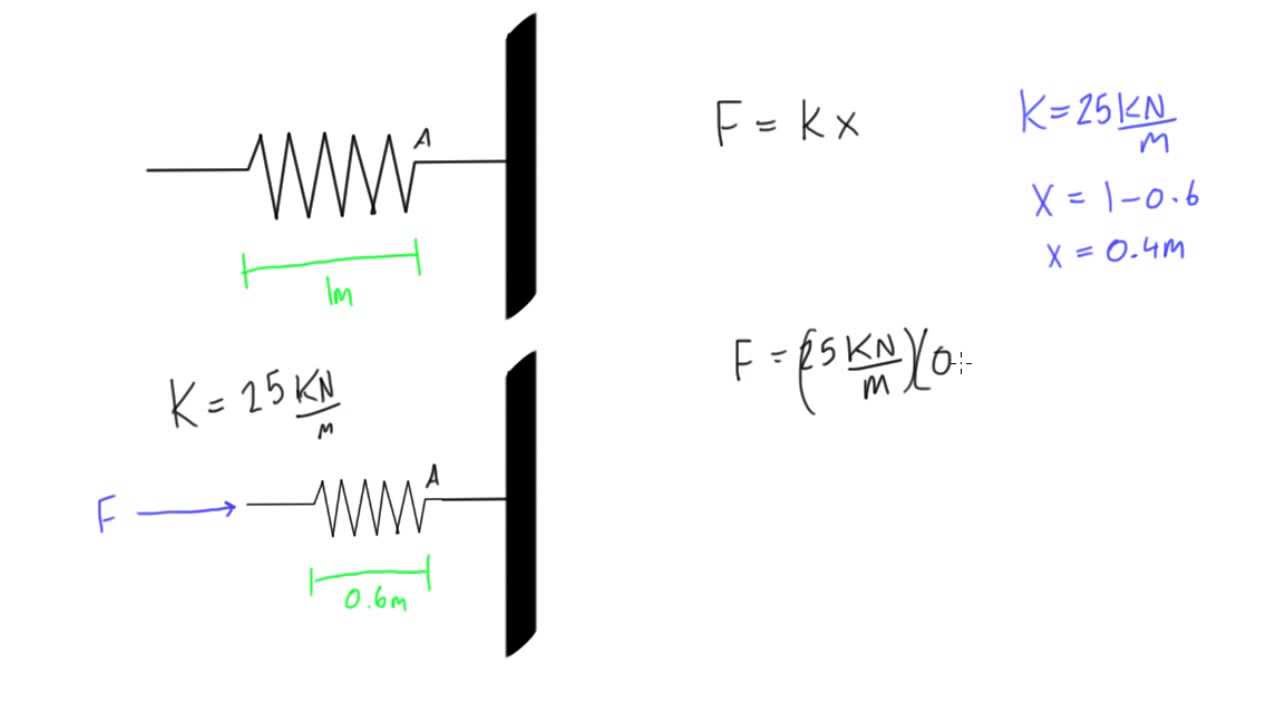
The work done by a constant force of magnitude f, as we know, that displaces an object by δx can be given asl: In the former kind, the magnitude and direction of the force remain unaltered. This case is a bit more complicated than the previous case. Θ is the angle between force and direction of motion; D = magnitude.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The net work done on an object (the work of the net force) is equal to the energy added to the object. In other words, work is equivalent to the application of a force over a distance. F = magnitude of the force applied. When the force f is constant and the angle between the force and the displacement s.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Work is done whenever a force moves something over a distance. The general formula for work and for determining the amount. ∫ a b f ( r ( t)) ∙ r ′ ( t) d t. Now , work done by this force is equal to the product of the magnitude of applied force and the distance through which the.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
F ( x, y) = x y i + 3 y 2 j a n d r ( t) = 11 t 4 i + t 3 j f o r 0. Work formula is made use of to compute work done, force, or displacement in any problem. Work done by a force. Where, f is the force applied; D.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Plug in the force and distance into the equation for work: If 1 joule of work is done then the formula for work comes out to be 1 j = 1 n.m. Work done = force × distance. Work done = force × distance [w = f~s] this is when: Keeping in mind that a friction force is a contact.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Energy transferred = work done = force x distance moved in the direction of the force. W = f s cos θ {\displaystyle w=fs\cos {\theta }} work is a scalar quantity, so it has only magnitude and no direction. In such a case, work (w) is equal to the force applied (f) multiplied by displacement (δx). Θ = is.





