Replace ‘ x ’ with ‘ time ’, ‘ y ’ with ‘ speed ’ and you get: Final velocity (v) of an object equals initial velocity (u) of that.
Equation For Velocity As A Function Of Time. A = acceleration, t = time. V ( t) = velocity of a particle at time t.
 Physics 170 Lectures, Fall 2005 From physics.upenn.edu
Physics 170 Lectures, Fall 2005 From physics.upenn.edu
V 0 = v − at. Velocity as a function of time and initial conditions. Here δ t ( m ) = m + λ p − α [ λ ( m )] is used;
Physics 170 Lectures, Fall 2005
T = v − v 0 /a. Impact velocity from given height. A = v − v 0 /t. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
 Source: wikihow.com
Source: wikihow.com
S ( t) = distance a particle travels from time 0 to t. Impact velocity from given height. Here are the main equations you can use to analyze situations with constant acceleration. V = u + a t. Show activity on this post.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
V 0 = v − at. > what is the formula for velocity as a function of time when an object was subject to constant acceleration? \rightarrow v=\int a,dt=a\int dt since the acceleration is. Replace ‘ x ’ with ‘ time ’, ‘ y ’ with ‘ speed ’ and you get: T = v − v 0 /a.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Then, you can find the velocity at exactly t = 4.0 seconds: Right now we have something in terms of time, distance, and average velocity but not in terms of initial velocity and acceleration. 2) the following are functions of time: S ( t) = distance a particle travels from time 0 to t. Speed as a function of time.
 Source: physics.upenn.edu
Source: physics.upenn.edu
V = u + a t. Show activity on this post. 2) the following are functions of time: Here δ t ( m ) = m + λ p − α [ λ ( m )] is used; ‘f’ of ‘ x ’ equals ‘ y ’, or.
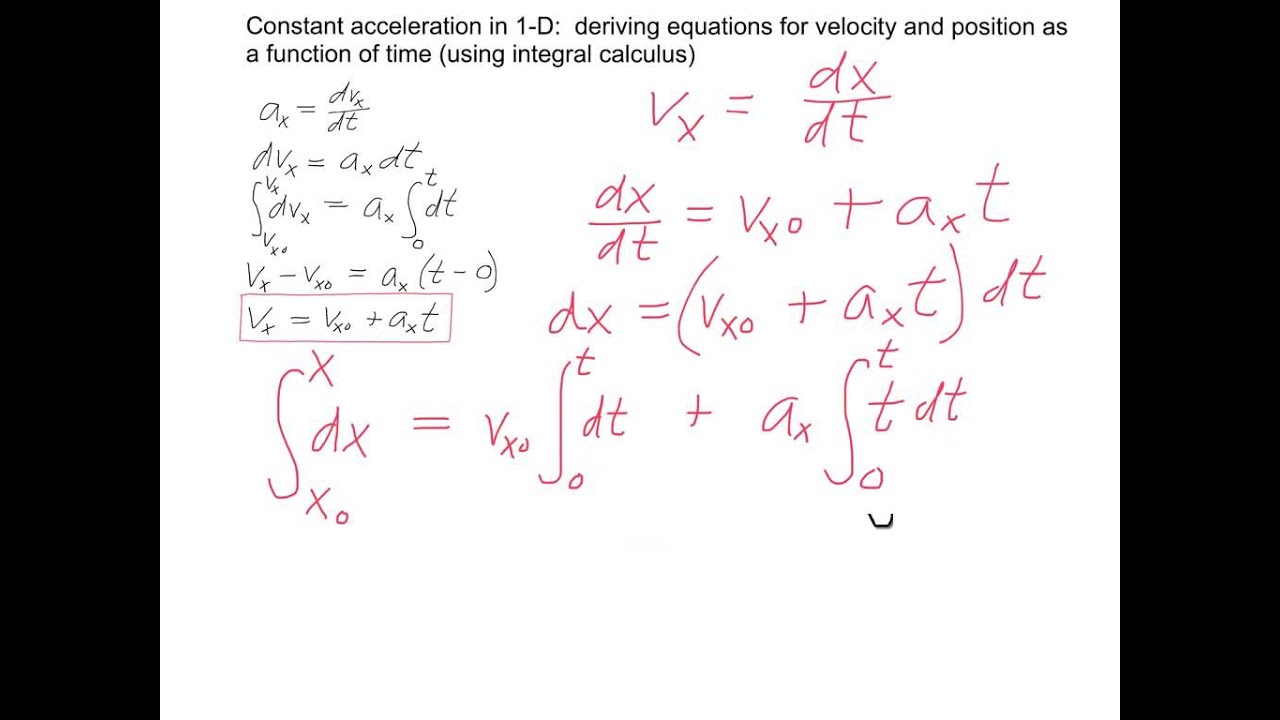 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
\rightarrow v=\int a,dt=a\int dt since the acceleration is. Right now we have something in terms of time, distance, and average velocity but not in terms of initial velocity and acceleration. A = acceleration, t = time. Now let’s take some values to understand the formula clearly. Using the equation for drag force, f = c d × ρ × v.
 Source: ppt-online.org
Source: ppt-online.org
V is the velocity field that the quantity is moving with. ( v i n s tan t) = lim t → 0 δ s δ t. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Start by finding the velocity function: V 0 = v − at.





